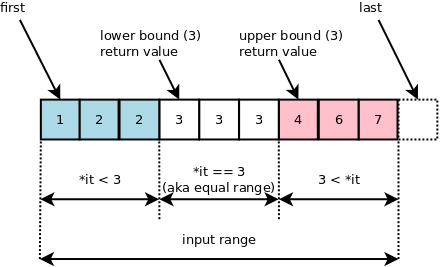
lower_bound는 0번째 배열의 원소부터 찾아서 어떠한 값의 "이상이 되는 위치"를 반환합니다.(시작부터 찾음)
upper_bound는 그 값이 시작되기 전의 위치를 반환합니다.(거꾸로 찾음)
lower_bound() or upper_bound() - 시작 주소값(v.begin() or a(배열)) 하면 int형으로 몇번째인지 알수있음
리턴이 iterator여서 *를 붙여주면 해당 위치의 값을 알 수 있음
코드
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
int a[5] = {1,2,2,2,3};
for(int i = 0 ;i < 5; i++)
v.push_back(a[i]);
int x = 2;
int c = (int)(upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x) - lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x));
int f = (int)(lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x) - v.begin()); // 주소를 빼줘서 몇번째인지 알 수 있음
int t = (int)(upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x) - v.begin());
int f2 = *lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x);
int t2 = *upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x);
printf("%d의 갯수 : %d, 시작되는 점 : %d, 끝나는 점 : %d\n", x, c, f, t);
printf("lower bound가 시작되는 점의 값 : %d, upper bound가 시작되는 점의 값 : %d\n", f2, t2);
c = (int)(upper_bound(a, a + 5, x) - lower_bound(a, a + 5, x));
f = (int)(lower_bound(a, a + 5, x) - a);
t = (int)(upper_bound(a, a + 5, x) - a);
f2 = *lower_bound(a, a + 5, x);
t2 = *upper_bound(a, a + 5, x);
printf("%d의 갯수 : %d, 시작되는 점 : %d 끝나는 점 : %d\n", x, c, f, t);
printf("lower bound가 시작되는 점의 값 : %d, upper bound가 시작되는 점의 값 : %d\n", f2, t2);
return 0;
}
/*
2의 갯수 : 3, 시작되는 점 : 1, 끝나는 점 : 4
lower bound가 시작되는 점의 값 : 2, upper bound가 시작되는 점의 값 : 3
2의 갯수 : 3, 시작되는 점 : 1 끝나는 점 : 4
lower bound가 시작되는 점의 값 : 2, upper bound가 시작되는 점의 값 : 3
*/값을 못찾을시(근방 지점 반환)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> v;
int main()
{
for(int i = 2; i <= 5; i++)v.push_back(i);
v.push_back(7);
// 2 3 4 5 7
cout << upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 6) - v.begin() << "\n";
cout << lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 6) - v.begin() << "\n";
cout << upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 9) - v.begin() << "\n";
cout << lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 9) - v.begin() << "\n";
cout << upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 0) - v.begin() << "\n";
cout << lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 0) - v.begin() << "\n";
}
/*
4
4
5
5
0
0
*/
'C++ > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| <알고리즘> 배열의 합(accumulate()) (0) | 2022.04.22 |
|---|---|
| <알고리즘> 배열 시계방향, 반시계 방향 회전(rotate()) (0) | 2022.04.22 |
| <알고리즘> 등차수열의 합 (0) | 2022.04.21 |
| <알고리즘> 에라토스테네스의 체 (0) | 2022.04.21 |
| <알고리즘> 모듈러 연산 (0) | 2022.04.21 |
